Tapping the Power of Continuous Digital Modeling for Industrial Lagoon Management
Lagoon systems are used by industrial operators to meet a variety of wastewater management requirements. But lagoons themselves must also be managed, both above and below the surface.
Conventional lagoon management and monitoring methods are highly manual and require significant coordination to get a comprehensive “as-is” representation of above ground and underwater features.
Recently, hydrographic survey capabilities have advanced greatly thanks to continuous digital 3D modeling technologies and techniques.
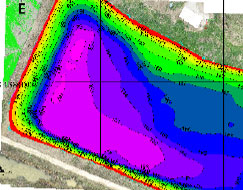
The ONE team has experience creating continuous digital 3D models of industrial lagoons that present a detailed view of the contoured terrain above and below lagoon water levels. These 3D models can be used to create a baseline for existing lagoon conditions, and periodic model updates can easily be made to detect changes in important metrics.
In addition, the 3D model interface can be accessed and shared online to support real-time collaboration across project teams. Unlike traditional methods that involve preparing figures with CAD software and emailing attachments that quickly become outdated, this method ensures team members have the most current information at their fingertips.
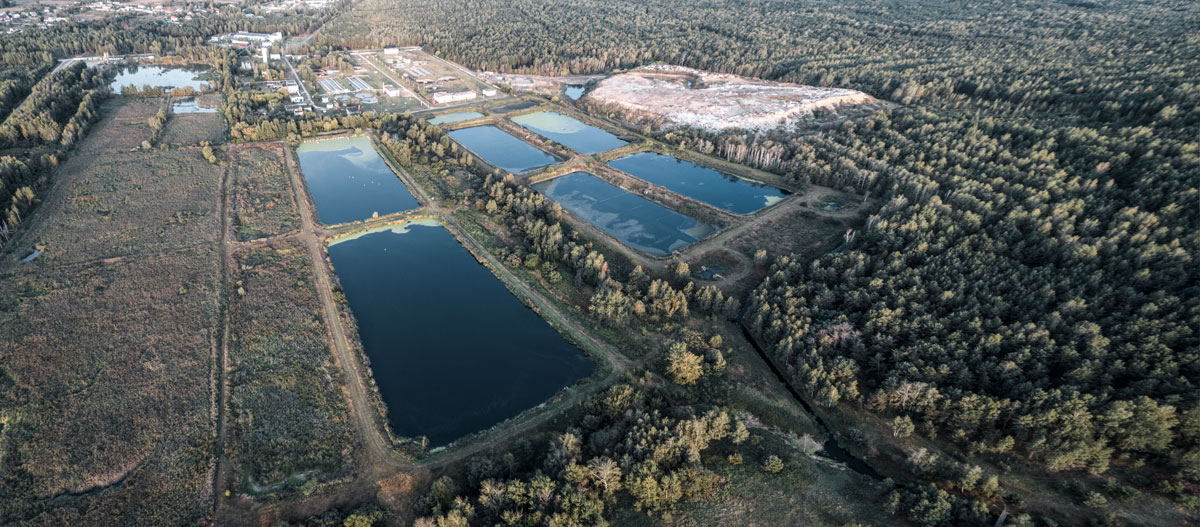
The ONE team recently put its continuous digital 3D modeling tools and expertise to work for one of the world’s leading manufacturers of wood products.
The project began with aerial mapping conducted with an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (commonly referred to as a drone). The aerial drone followed a prescribed flight pattern to achieve the specified ground sampling distance.
The mapping process then took to the water. A hydrographic survey of two client lagoons was performed using another type of drone – an unmanned surface vehicle (USV) or “drone boat.” The drone boat is equipped with state-of-the art technology such as: autonomous navigation (autonav) system, survey-grade Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) Receiver, and echosounder.
The drone boat’s autonav system provided precise control for the vessel to accurately follow prescribed grid patterns to detail lagoon terrain below the water surface. Manual measurements of sludge thickness at the bottom of the lagoons were collected along with surveyed ground control.
Georeferenced data collected from the drones were compiled and processed into 2D and 3D representations of the industrial lagoons. Ground control data were utilized to confirm the models were accurate and could be used for purposes such as:
- Taking precise sludge volume measurements.
- Calculating soil volumes needed to raise berms to specified elevations.
- Identifying specific utilities that will be affected as proposed construction plans are considered.
Ultimately, by leveraging these new models facilitated by the ONE team, the client can complete a variety of important lagoon management tasks more efficiently, with less risk and greater accuracy.